[Courtesy of GS E&C]
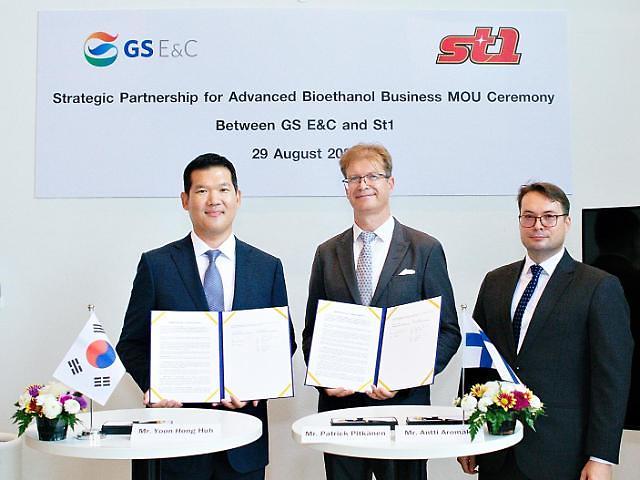
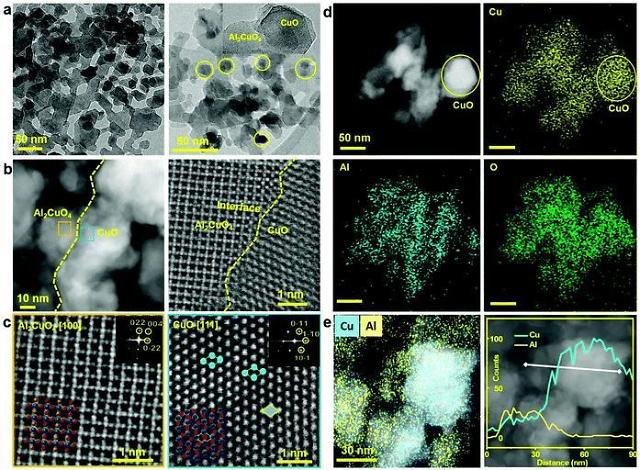
GS E&C said that a memorandum of understanding for technology development cooperation has been signed in Bangkok with St1, s a subsidiary of Finnish energy company St1 Oy, to produce bioethanol in Thailand, a major producer and exporter of cassava starch.
"We hope that cooperation between the two companies will signal the next-generation bioethanol production business using unused waste,"
GS E&C's new business division head Huh Yoon-hong said in a statement on August 31.
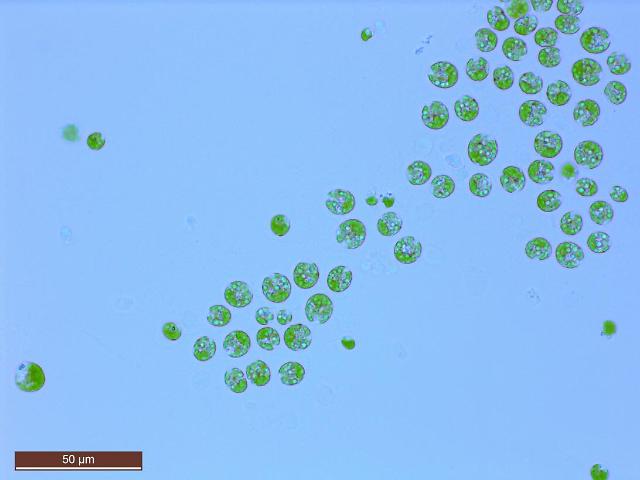
Cassava is a woody shrub extensively cultivated as an annual crop in tropical and subtropical regions for its edible starchy tuberous root, a primary source of carbohydrates. Cassava roots are exported as chips and pellets for ethanol fuel production, or as a raw material to extract starch. The processor extracting starch generates solid cassava pulp waste comprised of dry starch and lignocellulosic fibers.
The lignocellulosic fiber obtained after cassava starch extraction is potentially an ideal substrate for ethanol production. Bioethanol, usually made by fermenting corn or sugarcane, can be used as motor fuel or industrial raw material.